Synchronized Swimming: The Aquatic Ballet Revolutionizing Competitive Sports
Graceful movements, perfect synchronization, and breathtaking underwater acrobatics – synchronized swimming is redefining the boundaries of aquatic sports. This unique discipline combines the athleticism of swimming with the artistry of dance, creating a mesmerizing spectacle that captivates audiences worldwide. As we dive into the world of synchronized swimming, we'll explore its rich history, technical challenges, and growing influence on the global sports stage.
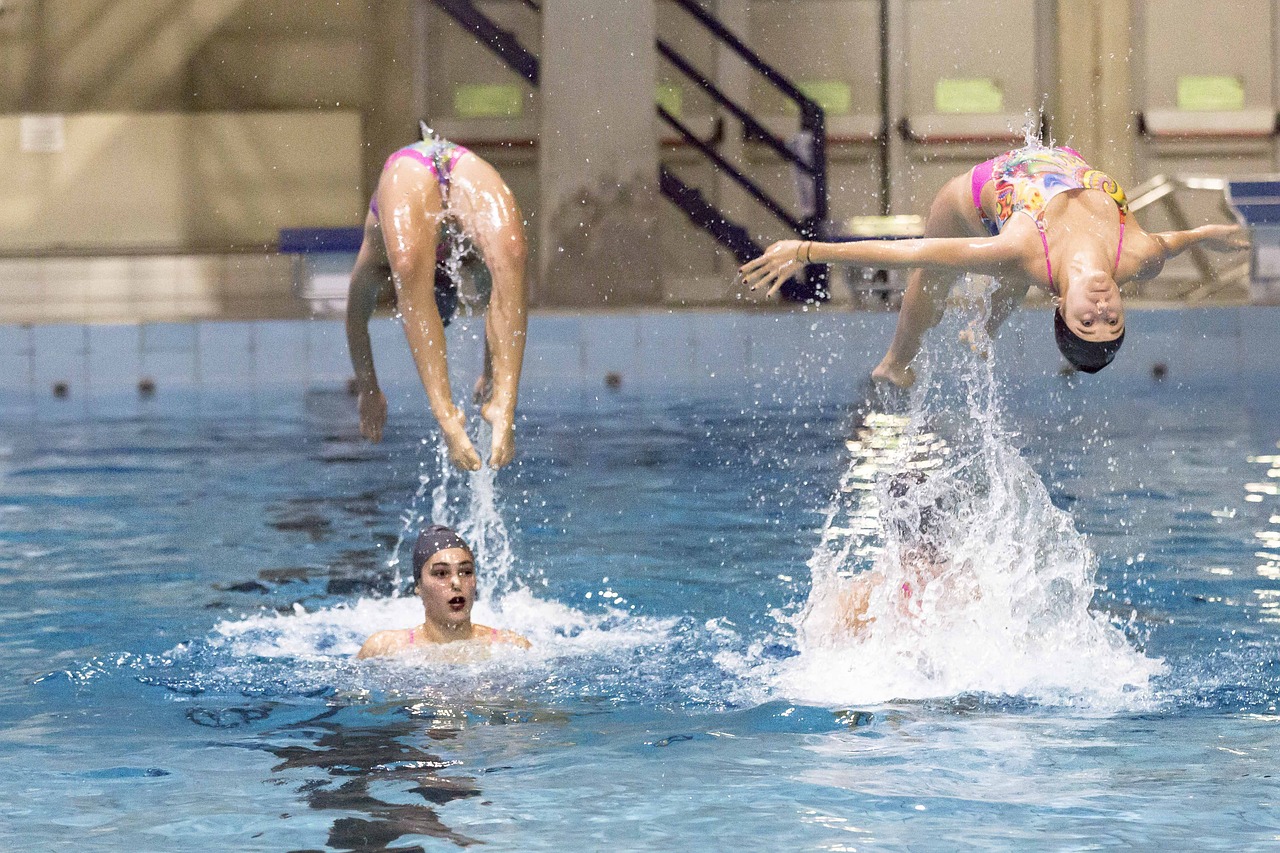
The Birth of an Aquatic Art Form
Synchronized swimming traces its roots back to the early 20th century, evolving from ornamental swimming and water ballets popular in Europe and North America. The sport’s modern incarnation began to take shape in the 1930s, largely due to the efforts of Katherine Curtis, an American swimming instructor who organized water ballet clubs at the University of Chicago.
Curtis’s work laid the foundation for what would become competitive synchronized swimming. She developed a system of water acrobatics and floating patterns, set to music, which formed the basis of the sport we know today. The term “synchronized swimming” was coined in 1934 when the Modern Mermaids, a group Curtis coached, performed at the Chicago World’s Fair.
As the sport gained popularity, it began to attract attention from Hollywood. Esther Williams, a competitive swimmer turned actress, popularized synchronized swimming through her aquatic musical films in the 1940s and 1950s. These glamorous portrayals helped spark public interest in the sport and contributed to its growing recognition as a legitimate athletic discipline.
The Technical Mastery Behind the Art
While synchronized swimming may appear effortless and graceful on the surface, it demands an incredibly high level of technical skill and physical conditioning. Athletes must possess a unique combination of strength, flexibility, endurance, and breath control to execute the complex routines that define the sport.
One of the most challenging aspects of synchronized swimming is the ability to perform intricate movements while upside down and partially submerged. Swimmers must maintain precise body positioning and execute choreographed movements in perfect sync with their teammates, all while holding their breath for extended periods.
The “eggbeater” kick is a fundamental technique in synchronized swimming, allowing athletes to maintain a stable vertical position in the water. This specialized treading motion requires tremendous leg strength and endurance, as swimmers often use it to support themselves and their teammates during lifts and other above-water maneuvers.
Breath control is another critical skill in synchronized swimming. Athletes must learn to manage their breathing efficiently, often holding their breath for up to a minute while performing strenuous underwater movements. This requires not only physical conditioning but also mental discipline and the ability to remain calm under pressure.
The Choreographic Challenge: Blending Art and Sport
At the heart of synchronized swimming lies the intricate choreography that transforms athletic movements into a cohesive artistic performance. Crafting a synchronized swimming routine is a complex process that involves careful consideration of music, theme, and technical elements.
Choreographers in synchronized swimming face the unique challenge of creating movements that are not only visually striking but also physically possible to execute in water. They must take into account factors such as buoyancy, resistance, and the limitations of underwater visibility when designing routines.
Music plays a crucial role in synchronized swimming, serving as both inspiration and timing mechanism for the athletes. Choreographers carefully select music that complements the theme of the routine and provides a rhythmic structure for the swimmers to follow. The integration of music and movement is so precise that swimmers often rely on underwater speakers to stay in sync during performances.
The artistic elements of synchronized swimming are balanced with rigorous technical requirements. Competitive routines are evaluated based on both artistic impression and technical merit, with judges assessing factors such as synchronization, difficulty of movements, and overall choreographic design.
The Evolution of Competitive Synchronized Swimming
Synchronized swimming made its debut as an Olympic sport at the 1984 Summer Games in Los Angeles, marking a significant milestone in its recognition as a competitive discipline. Initially, the Olympic program included only duet and solo events, but the team event was added in 1996, further expanding the sport’s profile.
The competitive structure of synchronized swimming has continued to evolve over the years. In 2017, FINA (the international governing body for aquatic sports) made significant changes to the sport, including renaming it “artistic swimming” at the international level. This change was intended to better reflect the athletic and artistic nature of the discipline and to make it more inclusive.
Today, competitive artistic swimming includes several event categories:
-
Solo: Individual routines showcasing a single swimmer’s skills and artistry.
-
Duet: Performances featuring two swimmers executing synchronized movements.
-
Team: Routines involving four to eight swimmers working in unison.
-
Mixed Duet: A relatively new category featuring male and female swimmers performing together.
-
Free Combination: A team event allowing for more creativity in formations and transitions.
These diverse event categories highlight the versatility of synchronized swimming and provide opportunities for athletes to showcase different aspects of their skills and artistry.
Training Regimens: The Path to Aquatic Excellence
The journey to becoming an elite synchronized swimmer is long and demanding, requiring years of dedicated training and practice. Athletes typically begin their training at a young age, often starting with a background in traditional swimming or gymnastics before specializing in synchronized swimming.
A typical training regimen for competitive synchronized swimmers includes:
-
Water Training: Several hours per day in the pool, focusing on technique, choreography, and endurance.
-
Land Training: Strength and conditioning exercises to build core stability, flexibility, and overall fitness.
-
Breath-holding Exercises: Specialized drills to improve lung capacity and breath control.
-
Flexibility Training: Stretching and gymnastics-inspired exercises to enhance range of motion.
-
Dance and Ballet: Classes to improve grace, body awareness, and artistic expression.
-
Mental Preparation: Visualization techniques and mental conditioning to enhance focus and performance under pressure.
The intensity of training increases as athletes progress to higher levels of competition. Elite synchronized swimmers often train for up to eight hours a day, six days a week, combining pool time with land-based exercises and recovery sessions.
The Global Impact of Synchronized Swimming
While synchronized swimming has traditionally been dominated by countries like Russia, China, and Japan, the sport is experiencing growing popularity and success in new regions. Nations such as Spain, Ukraine, and Canada have emerged as strong contenders in international competitions, contributing to the sport’s global development.
The inclusion of the mixed duet event in major international competitions has been a significant step towards gender inclusivity in synchronized swimming. This category, which pairs male and female swimmers, has helped challenge gender stereotypes and open up new opportunities for male athletes in the sport.
Synchronized swimming’s unique blend of athleticism and artistry has also made it a popular choice for aquatic shows and entertainment. Many water parks and resorts around the world feature synchronized swimming performances, helping to introduce the sport to wider audiences and inspire new generations of athletes.
Technological Advancements in Synchronized Swimming
As with many sports, technology is playing an increasingly important role in synchronized swimming. Advances in training techniques, performance analysis, and equipment design are helping athletes push the boundaries of what’s possible in the water.
Underwater cameras and motion capture technology are now used to analyze swimmers’ movements in detail, allowing coaches to provide more precise feedback and make subtle adjustments to technique and choreography. This technology has been particularly valuable in improving synchronization between team members and refining complex underwater maneuvers.
Innovations in swimwear design have also impacted the sport. Modern synchronized swimming suits are engineered to provide optimal flexibility and water resistance while enhancing the visual impact of the performance. Some suits incorporate special fabrics that change color or shimmer under water, adding an extra dimension to the artistic presentation.
Audio technology has seen significant improvements as well. Advanced underwater speaker systems ensure that swimmers can hear their music clearly throughout their routines, even when fully submerged. This has allowed for more complex choreography and better synchronization with the music.
Challenges and Controversies in Synchronized Swimming
Despite its growth and popularity, synchronized swimming faces several challenges and controversies. One ongoing debate centers around the subjective nature of judging in the sport. Critics argue that the scoring system, which combines technical merit with artistic impression, can be overly subjective and prone to bias.
Another challenge is the physical toll the sport takes on athletes. The demanding nature of synchronized swimming, particularly the frequent upside-down positions and extended breath-holding, can lead to a range of health issues. Concerns have been raised about the long-term effects of the sport on athletes’ bodies, particularly in terms of joint stress and potential neurological impacts from repeated breath-holding.
The sport has also faced criticism for its emphasis on a particular body type and aesthetic. There have been calls for greater diversity and inclusivity in synchronized swimming, both in terms of body types and cultural representations in choreography and music choices.
The Future of Synchronized Swimming
As synchronized swimming continues to evolve, several trends are shaping its future:
-
Increased Athleticism: Routines are becoming more physically demanding, with a greater emphasis on strength and acrobatic elements.
-
Technological Integration: The use of technology in training, performance analysis, and even in-pool effects is likely to increase.
-
Expanded Event Categories: There’s potential for new competitive formats, such as larger team events or mixed-gender team competitions.
-
Global Expansion: Efforts to promote the sport in new regions could lead to a more diverse competitive landscape.
-
Cross-disciplinary Influence: Increased collaboration with other artistic disciplines like dance and circus arts may lead to innovative new performance styles.
The Enduring Appeal of Aquatic Artistry
Synchronized swimming stands as a testament to the incredible potential of human movement in the aquatic environment. It challenges our perceptions of what’s possible in water, blending athletic prowess with artistic expression in a way that few other sports can match.
As the sport continues to evolve, it offers exciting possibilities for athletes, coaches, and spectators alike. The combination of physical challenge, artistic creativity, and teamwork makes synchronized swimming a uniquely compelling discipline, one that continues to captivate audiences and inspire new generations of aquatic artists.
From its origins as a form of water ballet to its current status as a highly competitive Olympic sport, synchronized swimming has come a long way. As it moves into the future, the sport promises to push the boundaries of human performance in water, creating ever more breathtaking displays of aquatic artistry.
Whether you’re a sports enthusiast, an aspiring athlete, or simply someone who appreciates the beauty of human movement, synchronized swimming offers a fascinating glimpse into the possibilities that arise when sport and art converge in the most unlikely of arenas – beneath the surface of the water.






